Introduction
Safety is one of the strongest reasons consumers choose inverter generators over traditional open-frame units. From cleaner electricity to intelligent protection systems and lower emissions, inverter generators are engineered to operate safely in homes, RV parks, campgrounds, and emergency environments. This article explains why inverter generator safety is superior and how it protects both users and electronics. For broader context, see the main Inverter Generator Guide along with Inverter Generator Efficiency Explained.

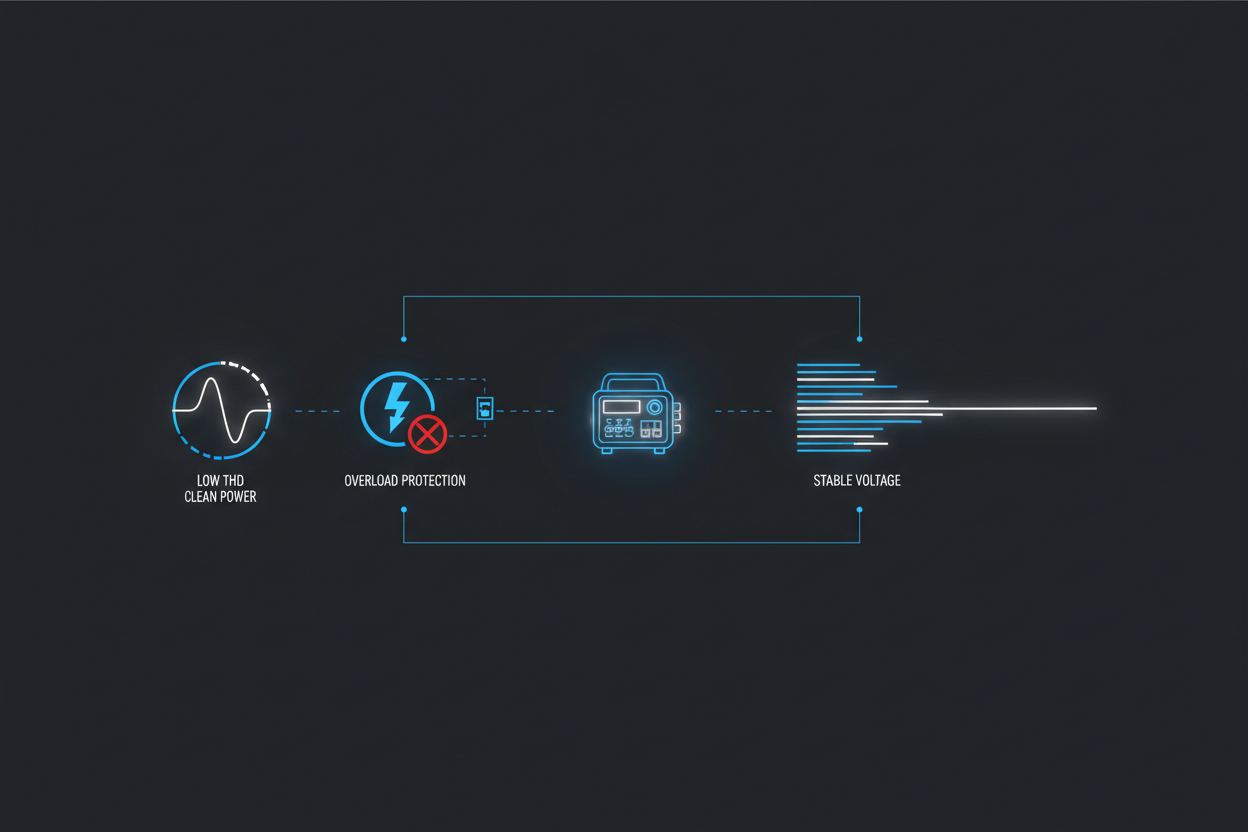
Why Inverter Generators Produce Safer Electricity
Traditional generators create AC power directly from engine rotation. When RPM fluctuates, the output becomes unstable, leading to:
- voltage spikes
- high harmonic distortion (THD)
- overheating in chargers
- malfunction of sensitive electronics
Inverter generators avoid these risks by digitally rebuilding power through three stages:
- raw AC
- DC conversion
- pure sine wave AC
This system ensures:
- stable voltage and frequency
- consistently low THD (often under 3%)
- clean, safe electricity for sensitive devices
For deeper waveform details, see Pure Sine Wave vs Modified Sine Wave and What Is THD in Generators?.
Built-In Overload and Low-Oil Protection
Most inverter generators include layered protection systems such as:
- overload shutoff
- low-oil automatic shutdown
- over-temperature protection
- advanced voltage regulation
- spark arrestor (required for many campgrounds)
This reduces the risk of overheating, electrical damage, or engine failure. For protection behavior under load, review Inverter Generator Load Handling.
Cleaner and Safer Exhaust Output
Inverter generators usually operate with:
- smaller, more efficient engines
- optimized combustion
- reduced emissions
- quieter exhaust output
These characteristics make them safer for:
- residential neighborhoods
- RV parks
- outdoor campsites
- tight operating spaces (always outdoors only)
For emissions and fuel-type behavior, see Dual-Fuel vs Gas Generators.
Lower Noise for Safer Operation
Loud engines can mask important warning signs such as:
- fuel or oil leaks
- worn wiring or connectors
- overheating
- engine knocking
Because inverter generators often run around 52–60 dB, abnormal sounds are easier to detect early. For quiet-operation engineering, explore Why Are Inverter Generators So Quiet?.
Safer for Electronics and Modern Homes
Modern homes and RVs rely on:
- smart appliances
- routers and modems
- computers and tablets
- medical equipment such as CPAP machines
- lithium battery power stations and chargers
These devices require clean, consistent voltage. Inverter generators protect them by:
- preventing voltage spikes
- reducing waveform distortion
- reacting automatically to fast load changes
- maintaining stable 120V/60Hz output
For more electronics-focused guidance, see Are Inverter Generators Safe for Electronics?.
When Traditional Generators Become Risky
Traditional open-frame generators can cause issues when:
- powering electronics without surge protection
- running close to maximum wattage for extended periods
- used in quiet neighborhoods with strict noise limits
- operated near tents, RVs, or enclosed spaces
- maintained inconsistently or operated with stale fuel
Their higher THD and unstable output can damage control boards, chargers, or sensitive RV systems. For real-world load examples, see How Much Power Do You Need?.
Conclusion
Inverter generators are safer because they deliver clean electricity, incorporate intelligent protection, run efficiently, and produce lower emissions and noise. For homes, RVs, and outdoor users relying on sensitive electronics, inverter generators offer unmatched safety and reliability compared with traditional open-frame units.
To continue learning about power quality, noise reduction, and reliability, explore the full Inverter Generator Guide and related articles such as THD in Generators, Why Inverter Generators Are So Quiet, and Maintenance for Inverter Generators.