Why Inverter Generators Are So Quiet
Introduction
Quiet operation is one of the biggest advantages of modern inverter generators for everyday users. Many buyers choose inverter models specifically because they produce far less noise than conventional generators. Lower sound levels matter in RV parks, campgrounds, suburban driveways, and quiet residential neighborhoods. This article explains the engineering behind inverter generator noise reduction and why these units run so quietly. Readers can explore more background inside the full Inverter Generator Guide.
Why Conventional Generators Are Loud
Traditional generators rely on fixed engine RPM to maintain sixty hertz output frequency under all loads. That constant high speed produces loud combustion noise, strong vibration, and aggressive exhaust pulses even at light loads.
- loud combustion noise
- high mechanical vibration
- strong exhaust output
- fluctuating sound levels during load changes
Even when powering only a few watts, a conventional generator must run near full speed. That behavior keeps noise levels close to those produced while running large appliances and tools. You can learn how this ties to waveform quality in our guide to THD in generators.
How Inverter Generators Reduce Noise
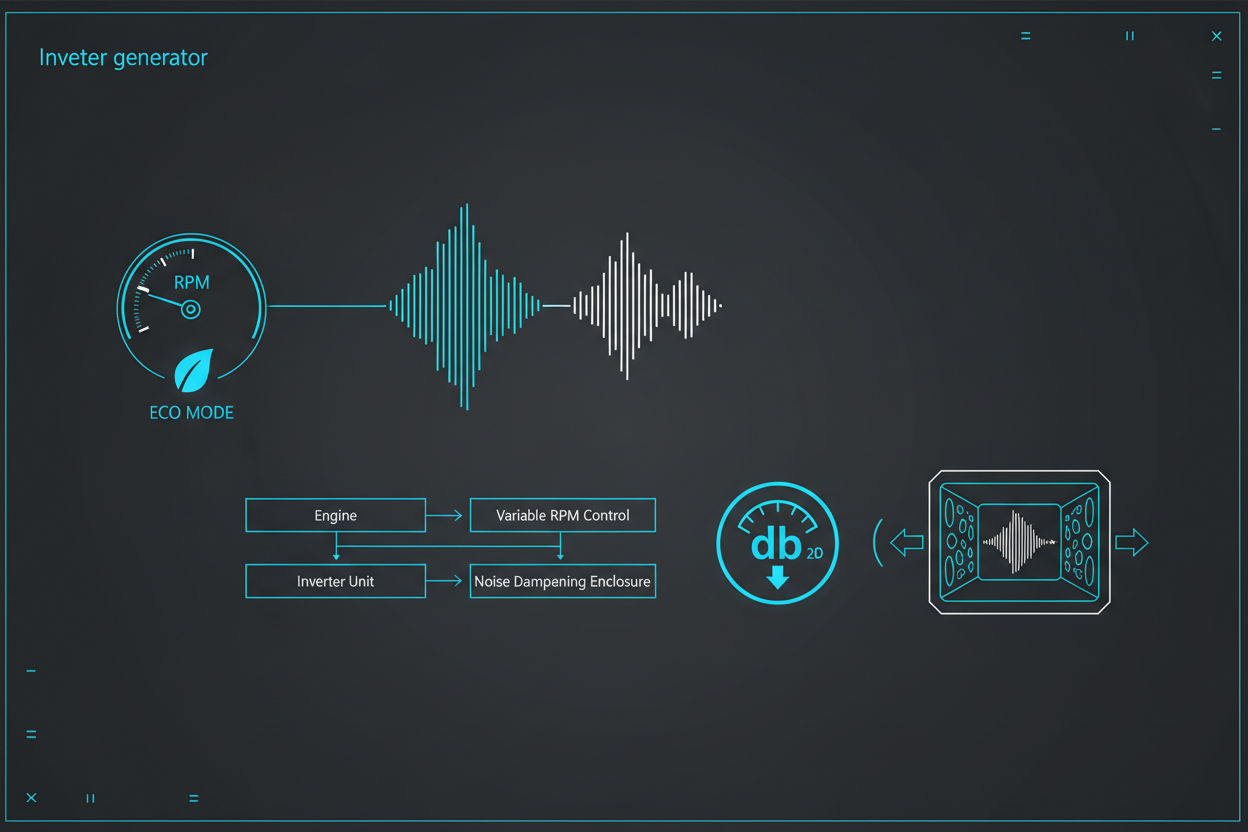
Inverter generators use a completely different architecture to keep sound output low across changing loads. Their noise reduction comes from three integrated systems that work together during operation.
- Variable engine speed (smart RPM control)
- Fully enclosed sound-dampening casing
- Advanced inverter microprocessor stabilization
These elements collectively reduce combustion noise, mechanical vibration, and exhaust resonance around the machine. A deeper technical overview appears in our inverter generator noise reduction technology guide.

Variable RPM: The Core of Quiet Performance
Inverter generators do not need to maintain a single fixed RPM for clean output. Instead, they automatically adjust engine speed based on real-time electrical load.
- light load → low RPM → very quiet operation
- medium load → moderate RPM with controlled sound
- high load → higher RPM but still quieter than open-frame units
Variable-speed technology is the single largest contributor to reduced noise in everyday situations. RPM flexibility also improves fuel efficiency, which we cover in inverter generator efficiency explained.
The Role of ECO Mode in Noise Reduction
ECO mode lowers sound levels further by slowing the engine whenever demand is low. The feature is especially helpful during nighttime or light-duty usage.
- engine speed slows during light loads
- combustion cycles become smoother and less abrupt
- vibration decreases around the frame
- fuel consumption and noise drop simultaneously
This behavior makes ECO mode ideal for charging electronics or powering a CPAP machine during camping trips. Runtime and fuel savings under ECO mode are detailed in our inverter generator fuel consumption guide.
Enclosed Acoustic Housing
Most inverter generators use a fully enclosed acoustic housing instead of an open steel frame. The shell surrounds the engine, alternator, and exhaust path with sound-dampening materials.
- contain mechanical noise from moving components
- reduce exhaust resonance within the enclosure
- minimize sound leakage through body panels
Manufacturers often add foam liners or layered plastics that absorb vibration and high-frequency noise. This enclosure design contrasts sharply with open-frame conventional generators.
Exhaust System Optimization
Modern inverter generators also rely on carefully tuned mufflers and exhaust routing. These components reshape sound before it reaches the surrounding environment.
- redirect exhaust airflow away from listeners
- dampen pulsation noise from combustion strokes
- reduce low-frequency rumble that travels long distances
Combined with lower engine RPM, optimized exhaust systems produce a smoother, less intrusive sound profile. RV owners can see additional outdoor use recommendations inside the RV Generator Guide.
Engine Size and Efficiency
Inverter generators typically use smaller displacement engines than comparable open-frame units. Their engines are designed for efficient combustion and reduced internal friction.
- smaller displacement engines with refined tuning
- more efficient combustion chamber designs
- lighter rotating components inside the crank assembly
These characteristics naturally lower mechanical noise and vibration for a given output wattage. Efficiency gains and runtimes are explored further in inverter generator runtime explained.
Sound Levels in Real Use Cases
A typical inverter generator operates at modest sound levels during normal outdoor usage. Measurements are usually taken at seven meters away on an open field.
- 52–59 dB at 25% load during light-duty operation
- 58–63 dB at 50% load under moderate everyday loads
These levels are comparable to a quiet conversation, household dishwasher, or calm office environment. For campers and RV owners, that difference is crucial for peaceful nights and friendly neighbors.
Comparing Noise Levels: Inverter vs Conventional
| Generator Type | Typical Noise (dB) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Inverter generator | 52–63 dB | quiet, variable RPM, enclosed housing |
| Conventional generator | 68–85 dB | loud, fixed RPM, open frame construction |
The difference is large enough that many national parks and RV resorts strongly prefer inverter generators. Campground rules and recommended distances are discussed in safe generator distance for camping.
Conclusion
Inverter generators achieve low noise levels using variable RPM control, ECO mode, optimized exhaust systems, and enclosed acoustic housings. These technologies work together to deliver quiet, neighbor-friendly power for camping, RV travel, and home backup.
Readers who want broader technical context about inverter design, THD, and clean power can continue with the complete Inverter Generator Guide.