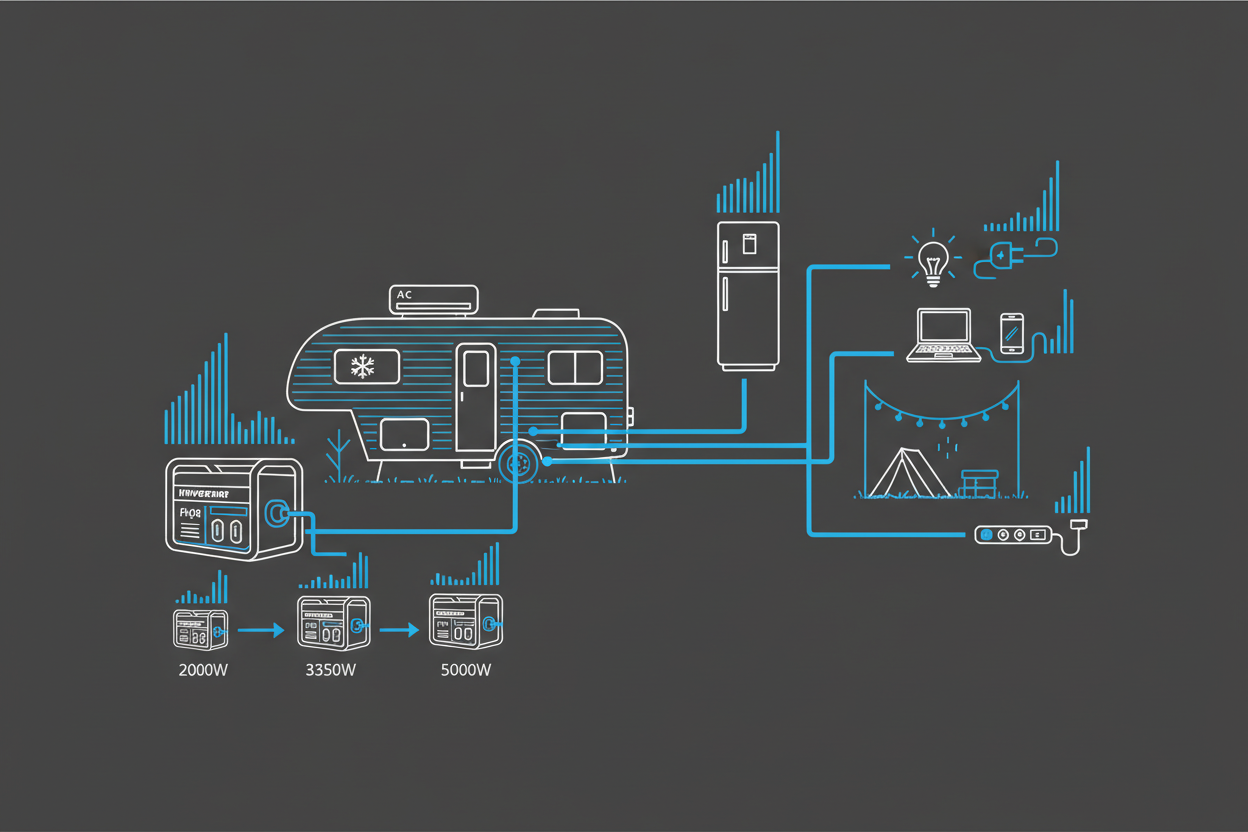
RV Generator Wattage Requirements: How Much Power Do You Really Need?
RVs use a mix of appliances with different power needs. Choosing the right generator wattage ensures safe cooling, cooking, charging, and lighting in every campsite.

RV Starting Watts vs Running Watts
Many RV appliances require higher wattage at startup. Air conditioners and microwaves create surge loads that your generator must handle without overload.
- Air conditioner: 1,600–2,300 starting watts
- Microwave: 1,000–1,500 watts
- Refrigerator: 600–800 starting watts
- Electronics & lighting: low, steady loads
Always size your generator based on the highest surge load.
Recommended Wattage for RV Types
- Small trailers: 2000–2400 watts
- Travel trailers: 3500–4500 watts
- Fifth wheels: 4500–6000 watts
- Motorhomes: 4000–7000 watts
Air conditioning is usually the deciding factor when sizing a generator.
Load Planning for RV Appliances
Running multiple appliances at once increases total wattage. Managing loads prevents overload and extends generator runtime.
- Run AC alone during compressor start.
- Use the microwave after AC stabilizes.
- Turn off water heaters during high load periods.
Soft Start for Lower Surge
Installing a soft start module reduces AC starting watts by up to 40 percent. This allows smaller generators to operate air conditioners more reliably.
Parallel Generator Option
If you need occasional high wattage, two smaller inverter generators in parallel offer flexible power without carrying a heavy unit.
Fuel Type and Wattage Output
Gasoline provides maximum wattage. Propane produces slightly lower output but offers longer storage life for off-grid RV camping.
Conclusion
Understanding starting watts, running watts, and appliance demand helps you choose the right generator size. With proper load management, your RV generator provides stable and efficient power for any trip.