Introduction
Choosing between an inverter generator and a traditional generator can be challenging. Both options offer portable power, but they differ greatly in noise, efficiency, electrical stability, and day-to-day usability. This comparison highlights the most important differences so users can choose the right option for home backup, camping, RV travel, or job sites. For full technical context, see the main Inverter Generator Guide.

Key Differences Between Inverter and Traditional Generators
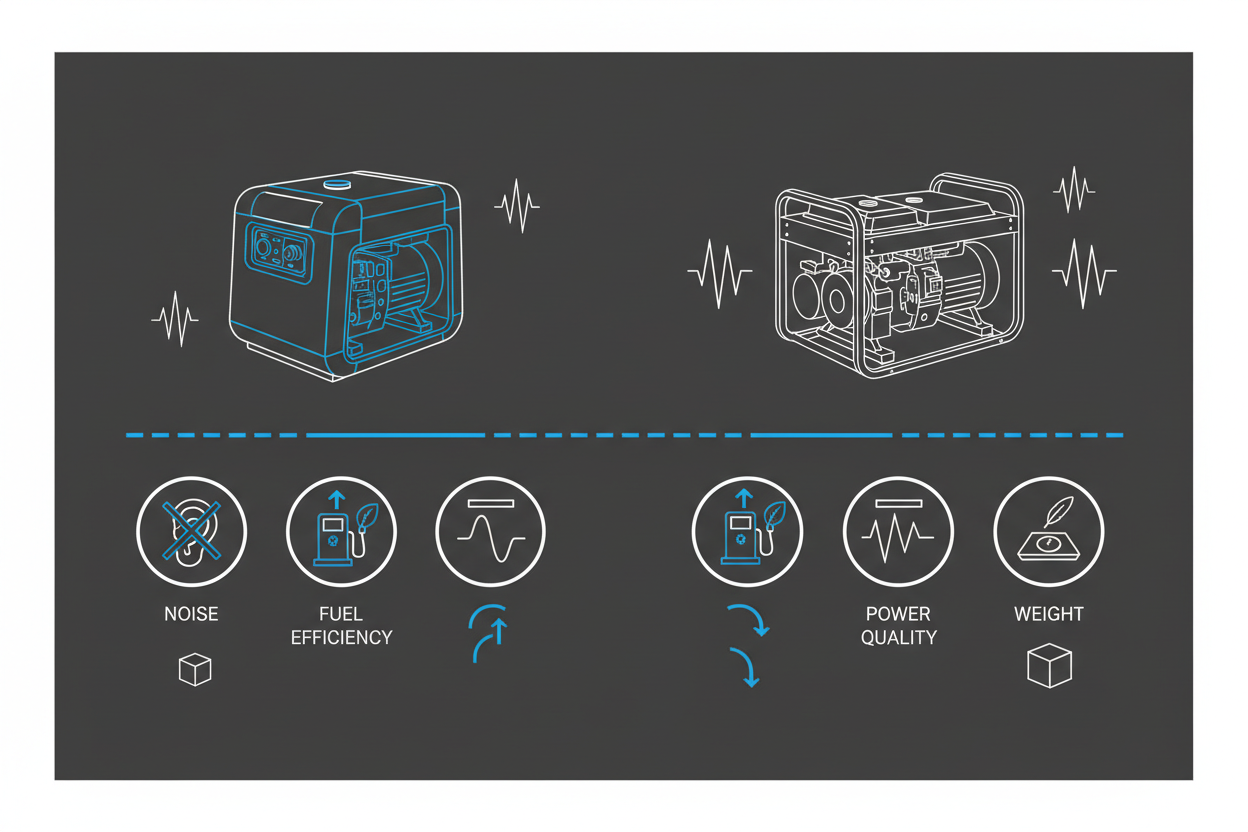
1. Power Quality: Clean vs Raw Electricity
Inverter Generator
- produces a pure sine wave
- THD typically under 3%
- safe for laptops, TVs, routers, CPAP machines, and chargers
Traditional Generator
- produces raw, unregulated AC
- THD can reach 10–25%
- unsafe for sensitive electronics
This makes inverter generators the clear choice for modern homes, RVs, and any electronics-heavy setup. For deeper waveform analysis, see What Is THD in Generators?.
2. Noise Levels
Inverter Generator
- typically 52–60 dB
- variable RPM = quieter operation
Traditional Generator
- typically 70–90 dB
- fixed RPM = full noise at all loads
For neighborhoods, RV parks, and campgrounds, inverter generators are overwhelmingly preferred.
3. Fuel Efficiency
Inverter Generator
- adjusts RPM based on load
- ECO mode reduces fuel burn
- delivers longer runtime per tank
Traditional Generator
- fixed RPM wastes fuel at light loads
- higher operating cost
Users who run generators frequently save far more with inverter models. For efficiency explanations, see Inverter Generator Efficiency Explained.
4. Portability and Size
Inverter Generator
- compact and lightweight (35–60 lbs)
- enclosed casing reduces vibration and noise
Traditional Generator
- bulky and heavy (70–120+ lbs)
- open-frame design
For RV travel, camping, and vehicle-based trips, inverter generators are dramatically easier to move and store.
5. Environmental Impact
Inverter Generator
- lower emissions
- more efficient combustion
- cleaner, quieter exhaust
Traditional Generator
- higher emissions and noise
- less efficient design
This makes inverter generators more suitable for residential areas and eco-sensitive campsites.
6. Price Differences
Inverter Generator
- higher upfront cost
- much lower fuel and maintenance cost over time
Traditional Generator
- lower initial price
- significantly higher long-term operating cost
Frequent users typically save more with an inverter model thanks to lower fuel burn and less mechanical wear.
When to Choose an Inverter Generator
Ideal for:
- RV travel
- camping and outdoor recreation
- home emergency backup
- quiet neighborhoods and parks
- electronics: TVs, laptops, routers, drones, medical devices
When to Choose a Traditional Generator
Possible for:
- construction job sites
- high-surge power tools
- users with very tight budgets
- occasional or limited use
These scenarios do not require clean sine wave power.
Conclusion
Inverter generators outperform traditional generators in nearly every category—noise, efficiency, safety, portability, and power quality. While traditional generators still serve well for job sites and heavy-duty tools, inverter models are the best choice for home, RV, and outdoor use where comfort and clean power matter.
To explore generator types, power quality, and related performance topics, continue with the full Inverter Generator Guide and supporting articles across the inverter generator blog cluster.