Solar vs Generator: Which Is Better for Camping?
Campers often choose between solar panels and generators for reliable outdoor power. Each option supports different camping styles, weather conditions, and wattage needs.
Understanding output, runtime, and limitations helps identify the best solution for each trip.

Solar vs Generator Output
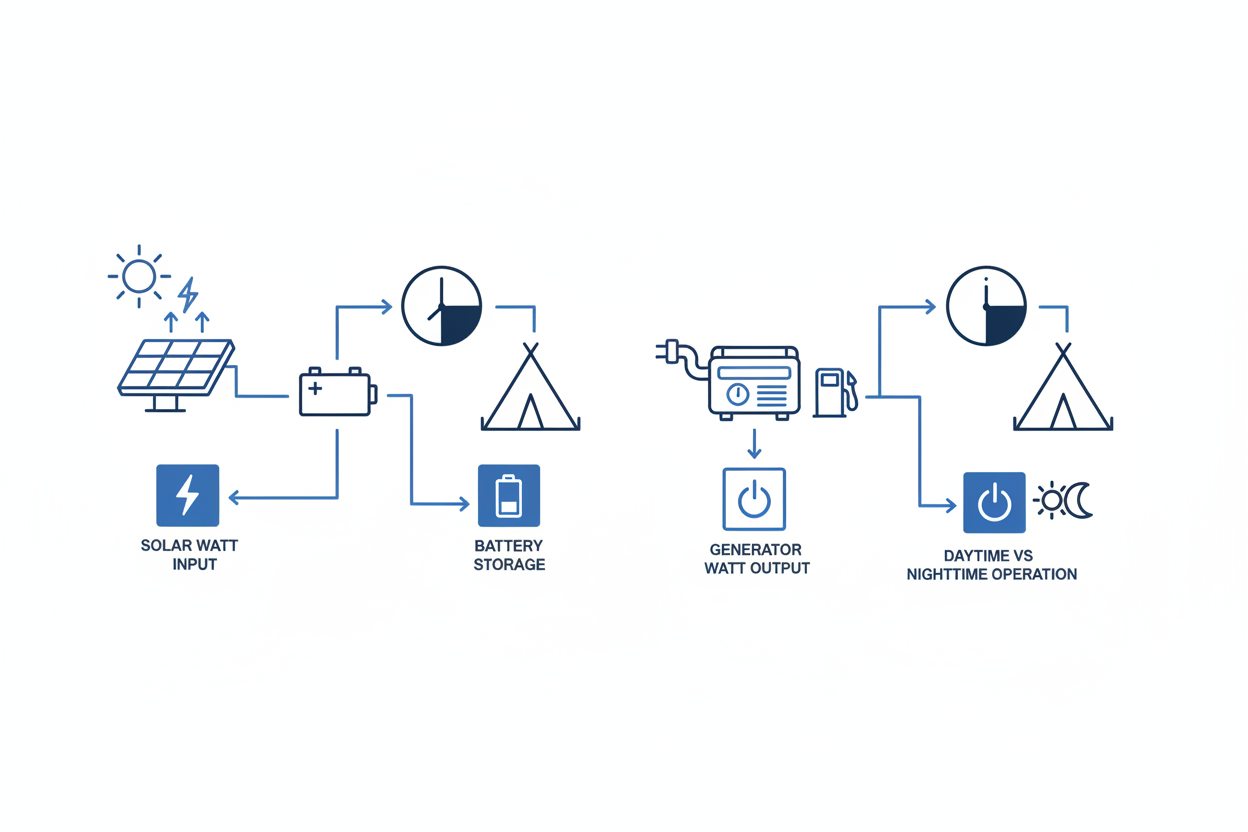
Solar panels produce limited wattage that depends on sun exposure. Generators deliver consistent power regardless of weather or time of day.
Most solar setups produce fifty to four hundred watts, while generators output one thousand to three thousand watts.
- Solar: 50–400W depending on panel size
- Generator: 1000–3000W depending on model
- Both: support lights, chargers, and small devices
When Solar Power Works Well
Solar excels during sunny weather with predictable daytime charging. Campers with minimal loads or extended stays benefit from steady renewable input.
Lightweight panels suit hikers, overlanders, and off-grid campsites with good sun angles.
- Charging phones and tablets
- Running LED lights
- Powering small coolers
- Recharging batteries and power banks
When a Generator Is the Better Choice
Generators provide high-wattage power for cooking, cooling, and medium appliances. They work in cloudy weather, at night, and during peak-demand activities.
Inverter models supply clean power for sensitive electronics and high-draw tools.
- Coffee makers and kettles
- Electric coolers or fridges
- Air pumps or compressors
- Projectors and CPAP machines
Hybrid Campsite Power
Many campers combine solar and generators for maximum flexibility. Solar handles daytime charging while the generator supplies high-load or nighttime power.
Hybrid setups reduce fuel use and extend quiet hours in sensitive campgrounds.
- Solar for lights and chargers
- Generator for cooking and cooling
- Battery storage for silent overnight use
Cost and Maintenance Considerations
Solar panels require minimal maintenance and offer long-term cost savings. Generators require fuel, oil changes, and occasional filter replacements.
Both options provide value depending on wattage needs and camping patterns.
Environmental Impact
Solar provides silent, emission-free power during daylight. Generators produce noise and exhaust but support essential appliances.
Campers seeking sustainable energy often start with solar and add a generator later.
Which Option Should Campers Choose?
The best choice depends on location, weather, and power demand. Solar works well for light loads and sunny sites, while generators handle heavy loads and unpredictable weather.
Many campers choose both for balanced capability and reliable off-grid power.
Conclusion
Solar panels and generators each offer advantages for camping. Solar provides silent renewable energy, while generators deliver consistent high-wattage output.
Combining both maximizes flexibility and ensures dependable power for every outdoor scenario.