How Inverter Generators Work: Inside the Power Conversion System
Introduction
Inverter generators deliver clean, stable, and efficient electricity using advanced electronic controls and multi-stage conversion. Unlike traditional generators that run at fixed engine speed, inverter models adjust output in real time based on demand. Understanding how inverter generators work helps you choose reliable power for home backup, RV air conditioners, and sensitive electronics. You can explore related topics inside our main Inverter Generator Guide.
What an Inverter Generator Does
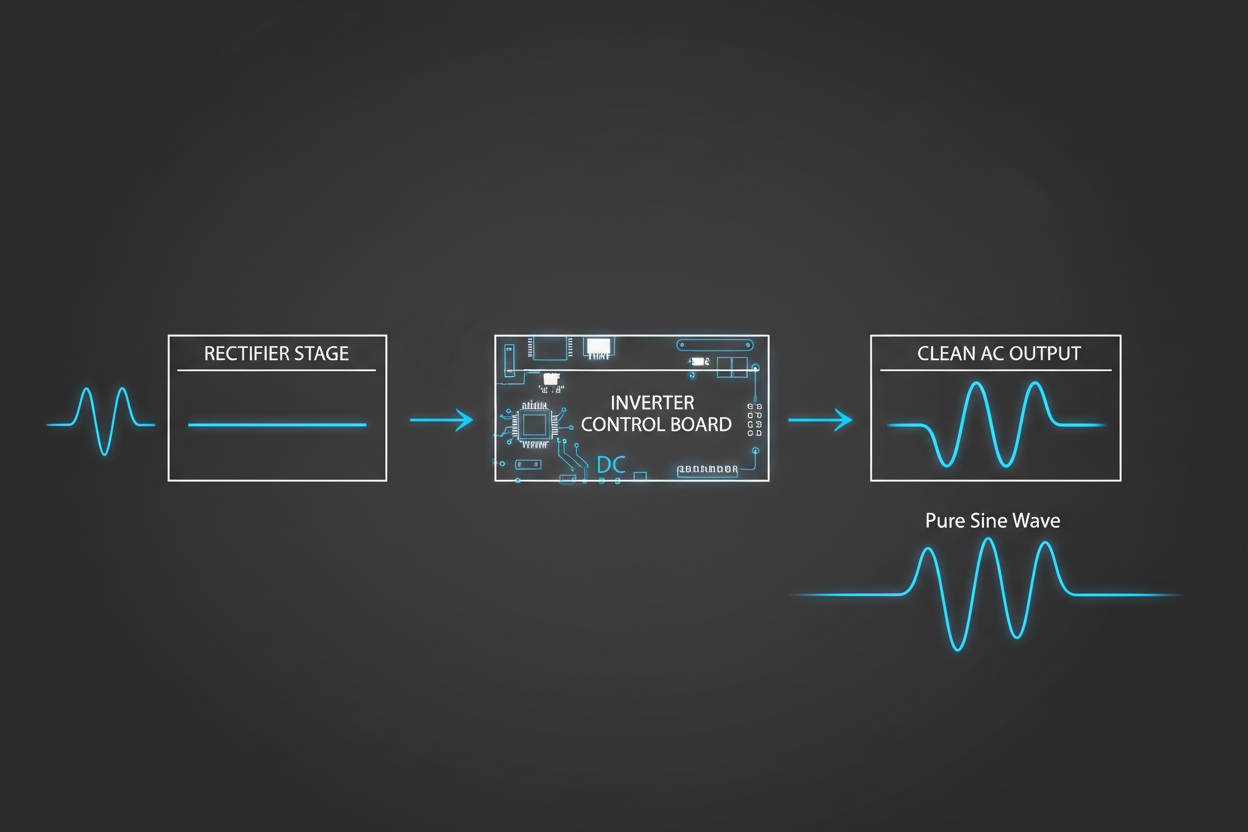
An inverter generator converts engine power into consistent, high-quality electrical energy for modern devices. The unit produces raw AC power, converts it into DC, then reconstructs it as a pure sine wave output. This controlled process stabilizes voltage and frequency while keeping distortion extremely low for sensitive loads.
This system protects modern electronics, reduces noise, and improves fuel efficiency during long runtime sessions. For more background on distortion, see our guide to THD in generators.

Three-Stage Power Conversion
1. AC to DC Conversion
The engine spins the alternator and generates raw AC power at variable frequency and voltage. This AC output is immediately converted into DC through rectifier circuits inside the inverter module. Conversion smooths voltage fluctuations and prepares the current for precise digital processing.
2. Digital Inversion
A microprocessor monitors load demand thousands of times every second during operation. The control board switches electronic components rapidly to build a controlled waveform from the DC bus. This digital processing sets the final frequency, voltage, and signal purity delivered to your outlets.
3. DC to Clean AC Output
Finally, the DC power is inverted back into a pure sine wave that closely matches grid electricity. The result is clean AC power with stable frequency and very low THD levels. This quality protects laptops, TVs, CPAP machines, and other sensitive electronics. You can compare waveforms in our guide on pure sine wave vs modified sine wave.
Why This Matters
Traditional generators tie output frequency directly to engine RPM, so small speed changes affect voltage and hertz. When RPM drops under sudden load, frequency drifts and voltage may sag or spike dangerously.
Inverter generators break this mechanical link by using digital reconstruction. Even when engine speed changes under varying loads, electronic controls hold output stable. This stability keeps phones, laptops, routers, televisions, CPAP machines, RV control boards, and refrigerators safer during extended use.
Clean power is one of the main reasons buyers upgrade from conventional generators to inverter technology.
How Engine Speed Control Works
Inverter generators adjust engine speed based on real-time load rather than running at one fixed RPM. When the load is light, the engine slows down to conserve fuel and reduce noise. When a device with high starting watts activates, the system quickly increases speed to cover the surge.
Benefits include lower fuel usage, reduced engine wear, quieter operation, and smoother voltage delivery to connected devices. You can learn more about efficiency behavior in our article inverter generator efficiency explained.
Understanding Harmonic Distortion
THD, or Total Harmonic Distortion, measures how pure an AC waveform is compared with an ideal sine wave. Lower THD numbers mean cleaner electricity and less stress on electronic power supplies.
- Inverter generators: <3% THD under normal operating conditions
- Traditional generators: 15–25% THD depending on design and load
High THD can cause overheating, flickering screens, buzzing audio, and long-term damage to sensitive electronics. Inverter generators keep THD low by digitally reconstructing sine waves instead of relying only on mechanical regulation.
Why Inverter Generators Are Quieter
Noise reduction is one of the strongest advantages of inverter technology for homeowners and campers. Inverter generators run at flexible RPM instead of full throttle, which immediately lowers sound levels.
- run at variable RPM matched to load
- use insulated housings and compact enclosures
- include advanced mufflers and exhaust routing
- reduce vibration using tuned anti-vibration mounts
Most inverter models operate between 52–65 dB, suitable for campgrounds, RV parks, and residential neighborhoods. For a deeper dive into sound engineering, see inverter generator noise reduction technology.
Fuel Efficiency Advantages
Inverter generators only burn the fuel required for the current load instead of full capacity. When ECO mode is enabled, the engine automatically reduces RPM during light usage periods.
This smart control delivers longer runtime, lower cost per hour, cleaner emissions, and extended engine lifespan. You can study detailed consumption behavior in inverter generator fuel consumption explained. Runtime planning tips appear in inverter generator runtime explained and our inverter generator cost guide.
Stable Power During Sudden Load Changes
Many appliances draw extra watts when starting, such as air conditioners, pumps, and microwaves. Inverter generators respond instantly to these surges using sensors and microprocessor control.
- sensors detect the new load
- the microprocessor increases RPM and output
- voltage remains stable at the outlets
- output frequency stays within safe limits
This stability helps run high-demand devices without flicker, brownouts, or shutdowns. RV owners can explore air conditioner compatibility in the RV AC compatibility guide.
Practical Applications
Home Backup
Homeowners use inverter generators to power refrigerators, lights, routers, and work-from-home electronics during outages. These scenarios are covered in detail inside our Home Backup Generator Guide.
RV Travel
RV travelers rely on inverter generators to start and run thirteen point five thousand BTU air conditioners. They also keep batteries charged and electronics safe on the road, as explained in the RV Generator Guide.
Camping
Campers use inverter generators for quiet lighting, phones, cameras, and small appliances at remote sites. For more outdoor strategies, visit the Camping Generator Guide.
Conclusion
Inverter generators combine smart electronics, efficient engine control, and multi-stage power conversion into one compact package. Understanding how inverter generators work explains why they are safer for electronics, quieter in operation, and more fuel-efficient than traditional generators. For home backup, RV adventures, and camping trips, inverter generators deliver reliable and stable performance.
Readers who want deeper technical detail can continue inside the complete Inverter Generator Guide.